
Ever wonder why your internet connection or cable TV signal is crystal clear one moment and frustratingly fuzzy the next? The answer might be lying right under your nose, or rather, behind your TV set: the coaxial cable. As we delve into the world of coax cables, we’ll unravel their types and uses, helping you make an informed choice for your next DIY project or tech upgrade.
Coax cables aren’t just wires; they’re the lifeline of your home entertainment system. Understanding their nuances could mean the difference between a perfect movie night and a pixelated mess. But what is coax cable used for? Let’s get started and explore the fascinating world of coax cables together.
Understanding Coax Cable Basics
Having grasped the importance of coax cables, it’s time to delve more into their functionality. Below, we’ll unravel the technicalities of these cables, bring light to their key components, and explain why they’re a staple in the world of internet and cable TV connections.
What Is Coaxial Cable?
Coaxial cable, often referred to as coax cable, plays a fundamental role in transmitting radio frequency signals. It’s engineered to deliver information rapidly while minimizing the loss of data due to attenuation level, and safeguarding against electromagnetic interference. It’s a staple in the realm of telecommunications, playing a pivotal role in internet connections, cable TV, and radio transmissions.
Key Components of Coaxial Cables
Breaking the coaxial cable down, I find three key components as integral parts. First, we have the center conductor which carries the electrical signal. This can be solid or stranded depending on the type of coaxial cable. Next, we have the dielectric insulator, a layer that separates the inner conductor from the outer shielding. It’s this dielectric that keeps the signal on track and staves off signal loss.
Lastly, there’s the outer conductor or shield, often made of woven copper or aluminum. It serves two main functions: it forms a return path for the signal, and more importantly, it protects the cable from electromagnetic interference.
Some of you might also count a fourth component, the protective outer jacket. It’s generally made of plastic and safeguards the integrity of the cable from environmental factors.
Whether for a DIY project or a professional installation, understanding these basics helps comprehend performance variations among different coax cable types. For instance, a thicker dielectric layer or a tighter cable weave reduces attenuation, considerably enhancing performance. And for the tech-savvy, custom wiring harness options like Cloom or BNC connectors offer bespoke solutions for specific requirements.
So, grasping these fundamentals equips you with the knowledge to optimize your cable TV signal or internet connection. Decoding the jargon, understanding the mechanics, you’re set to navigate the world of coax cables.
Different Types of Coaxial Cables
Within the stable of coax cables, there exists variety, each boasting unique features, benefits, and uses.
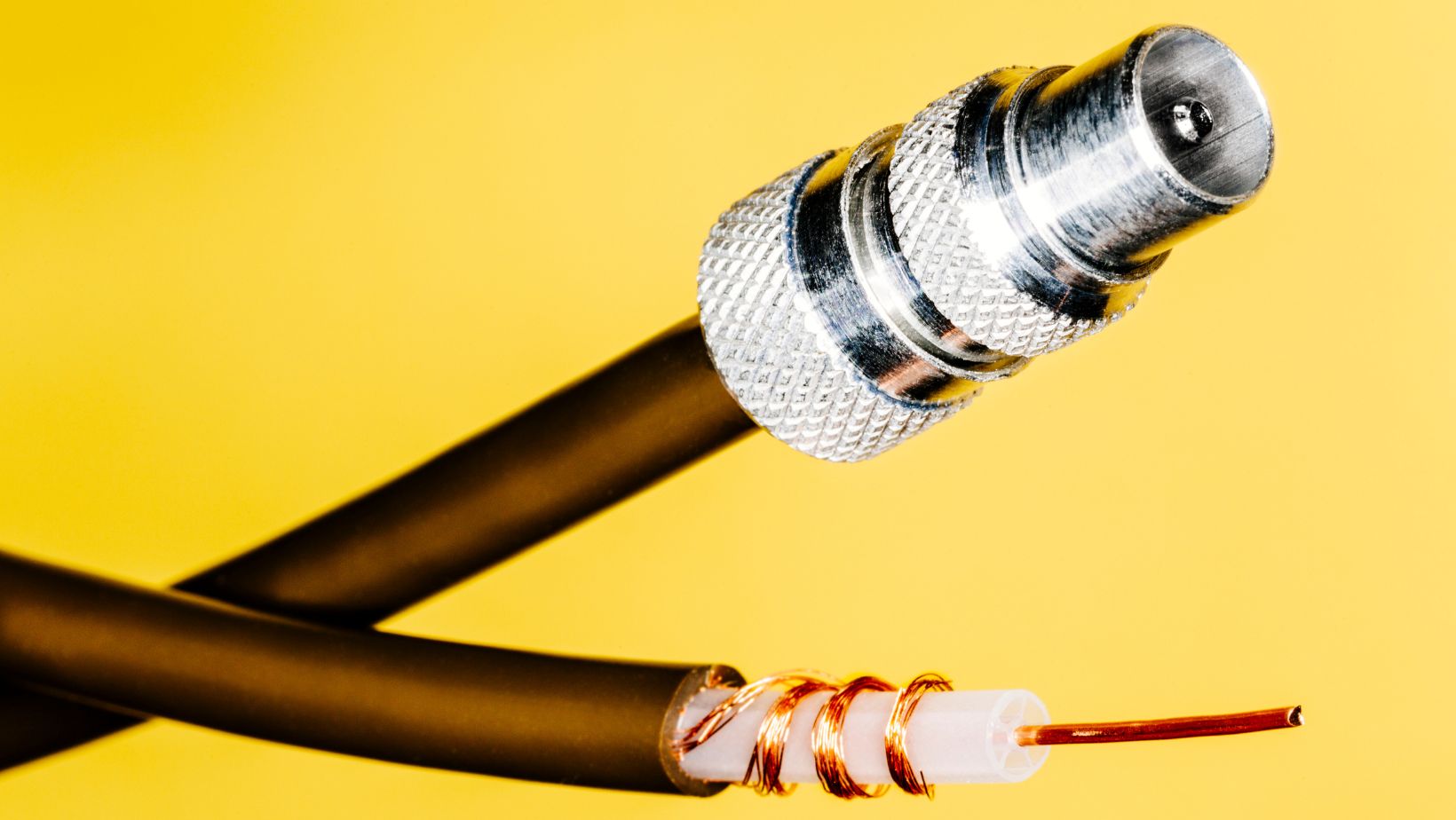

We delve into three main types, each differentiated by their varying attenuation levels, susceptibility to electromagnetic interference, and suitability for specific applications.
RG-6 Coaxial Cables
RG-6 coaxial cables resonate as the popular choice for most household uses. I find them primarily in home entertainment systems, notably satellite television and cable internet connections. Their characteristic thick dialectric insulator minimizes signal loss, optimizing performance especially for high bandwidth usage. An RG-6, compared to its counterparts, handles higher frequency signals and guarantees lower attenuation levels. If a custom wiring harness is in the plan, consider the RG-6 to be a supreme candidate.
RG-59 Coaxial Cables
RG-59 coaxial cables often serve analog or CCTV (Closed Circuit Television) installations in particular. They are thinner and more flexible than the RG-6 which makes them handy in cramped situations or where turn radii are small. However, my warning is that they carry a higher attenuation level, which could dampen signal strength over long distances. When accuracy isn’t a priority, like with analog TV signals, the RG-59 proves brilliant. Moreover, when combined with high-quality connectors like BNC or Cloom, their performance notably improves.
RG-11 Coaxial Cables
Lastly, the RG-11 coaxial cables are the heavyweight of the group, tending to longer distances and lower signal loss. Dealing with crowded signal routes is where they shine – long stretches of cable, or when a signal is split multiple times. Their dense construction wards off electromagnetic interference, thus preserving signal integrity. While they might be stiffer and challenging to work with, the RG-11’s resilience to signal decay over distance and interference make them a worthwhile investment. These applications especially qualify for utilizing custom wiring harness benefits.
Selecting the Right Coaxial Cable
To ensure an efficient and interference-free connection, it’s crucial to choose the right type of coaxial cable. Let’s dive into some factors to consider and find out the best uses for each type of cable.
Factors to Consider
When choosing a suitable coaxial cable, you’ve got to evaluate three main factors: attenuation level, cable flexibility, and resistance to electromagnetic interference. Firstly, you should look at the attenuation level. It directly impacts the intensity of the signal that reaches the receiving end. A higher attenuation level indicates that the signal will lose its strength over long distances or at higher frequencies. RG-6, RG-59, and RG-11 cables have different levels of attenuation, so your choice critically depends on your specific requirements.
Secondly, consider the cable’s flexibility in your setup. RG-59, for example, is more flexible than RG-6 and RG-11, which stands out in setups that require a considerable amount of bending and rounding.
Thirdly, think about the cable’s resistance to electromagnetic interference. RG-6 is specifically designed to counter this, which makes this cable type the perfect choice for high bandwidth usage where interference could significantly impact performance.
Lastly, connectivity options like BNC or Cloom custom wiring harnesses can optimize the performance of these cables by reducing loss and improving durability.
Ideal Uses for Each Type
RG-6 is an ideal choice for high bandwidth requirements, excelling in applications where it’s required to transmit large amounts of data without sacrificing signal strength.
RG-59, due to its flexibility and lower cost, finds its optimal usage in analog or CCTV installations where you need to round corners or fit inside small conduit without risk of damaging the cable.
RG-11, intended for long-distance connections, maintains its signal integrity over extensive ranges. Its best use would be where long cable runs are needed, and protection against signal loss is a priority, such as in larger buildings or outdoor installations.
By understanding these aspects, you can make informed decisions about the best coaxial cable choice for your specific requirements.
Maintaining Your Coaxial Cables
Third step, after choosing the perfect coax cable and harnessing it using connectors like BNC or Cloom, is to correctly install and maintain them. Doing so keeps the attenuation level and electromagnetic interference in check.
Tips for Proper Installation
Installing your coax cables correctly significantly impacts their performance and lifespan. Here are some points to remember:
- Always confirm the cable’s directionality, if applicable, before installation. This step ensures optimal signal transfer.
- Use quality coax cable tools for cutting and stripping, which maintains the integrity of the cable and reduces attenuation.
- Avoid kinking or bending the cable excessively. A gentle curve with a minimum radius of five times the cable diameter maintains the cable structure and minimizes signal loss.
- Consider using a custom wiring harness for a neater and more organized setup. This approach also prevents cable damage and reduces electromagnetic interference.
- Increased Attenuation: This problem often results from cable damage or wear and tear. You can replace damaged sections or the entire cable, if necessary, to resolve this issue.
- Severe Electromagnetic Interference: Proper grounding is usually the fix. And in extreme cases, consider switching to a coax cable with a better shielding factor.
- Loose or Corroded Connectors: Regularly check connections and replace faulty ones. Use BNC or Cloom connectors for a reliable and low-maintenance solution.
Conclusion
So, knowing your coax cables isn’t just tech jargon—it’s crucial for ensuring top-notch connections. Remember, it’s not just about picking any cable. You’ve got to consider factors like attenuation, flexibility, and resistance to electromagnetic interference. Whether it’s RG-6, RG-59, or RG-11, each has its unique strengths and applications. Don’t overlook the power of custom wiring harness options like BNC or Cloom connectors. They’re game-changers for boosting performance. And once you’ve got your perfect cable, don’t forget about installation. It’s all about the details—confirming directionality, using the right tools, and avoiding unnecessary bending. And of course, keep an eye out for common issues. Regular maintenance can make all the difference in achieving optimal cable performance. With the right knowledge and care, you’re all set for a seamless, interference-free connection.











